Relationships between Omega-3 and ADHD
It is estimated that there are more than 40,000 children and teenagers suffering from ADHD in Hong Kong, and the general treatment methods are mainly drugs and behavioral therapy. Medications can suppress children’s activity levels and impulsive behaviors, and behavioral therapy can reduce the chance of children developing rebellious behaviors.
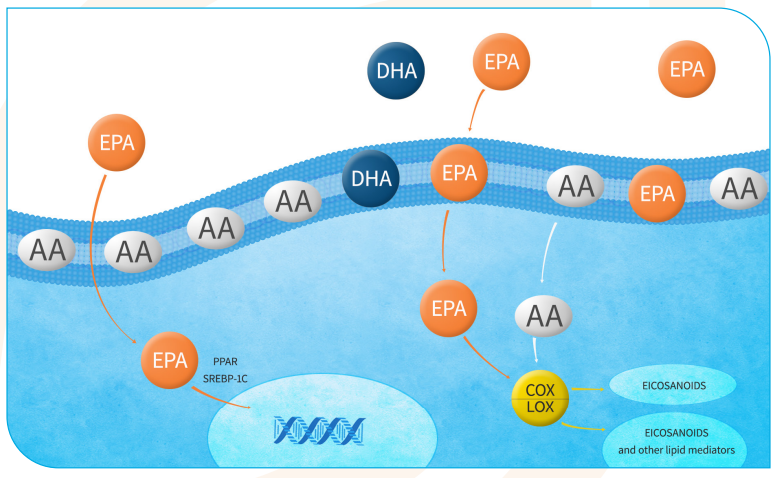
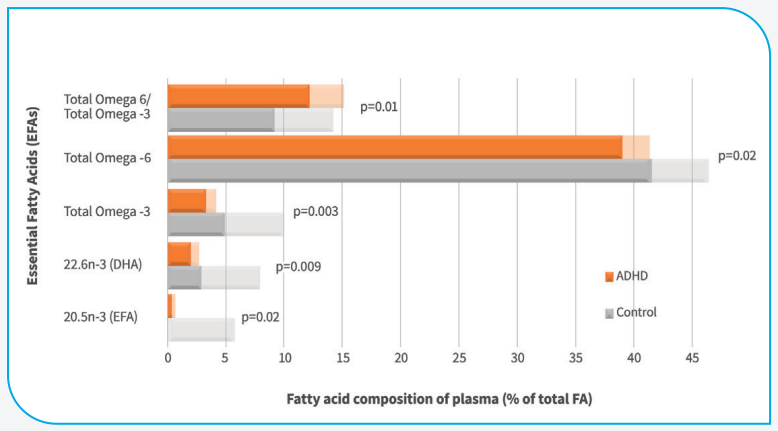
In recent years, many large-scale studies have found that children’s intake of Omega-3 fatty acids has a very high correlation with the prevalence of ADHD. According to research, children with ADHD have much lower amounts of Omega-3 fatty acids in their bodies than children without the disease. In recent years, more and more studies have found that appropriate supplementation of fish oil in children with ADHD may improve the patients’ concentration and alertness.
Have you or your children faced the following problems?

- Often rushing to tell the answer
- Frequently interrupts other people’s conversations
- Often harass others
- Often unable to participate in activities quietly
- High energy and unable to calm down
- Talkative

- Inability to pay attention to details and careless mistakes
- Difficulty maintaining concentration
- Frequently not paying attention to what others are saying
- Frequently fails to complete assigned tasks
- Lack of organization in doing things, starting from the beginning and ending at the end
- Afraid of using my brain

- The body often twists and turns
- Can’t sit still
- Frequent running and crawling
- Things are often lost
- Often distracted by external interference
- Frequently forgetting what needs to be done every day
Why does ADHD exist?
The answer is in the genes. Specific innate genetic differences have been found in many individuals with hyperactivity disorder,
This reduces the efficiency of enzymes that metabolize long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids.
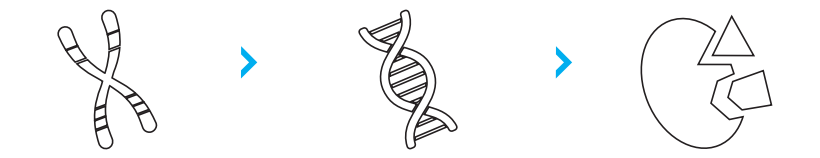
- FADS-1 and FADS-2 genes found in the genetically “hot” ADHD region (on chromosome 11)
2. Genetic code for saturases (Delta-5 and Delta-6), which convert essential fatty acids into long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids
3. In ADHD, different alleles create different forms of the enzyme, which metabolize long-chain omega fatty acids less efficiently


 中文 (中国)
中文 (中国) 中文 (香港)
中文 (香港)