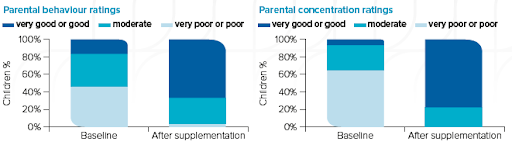
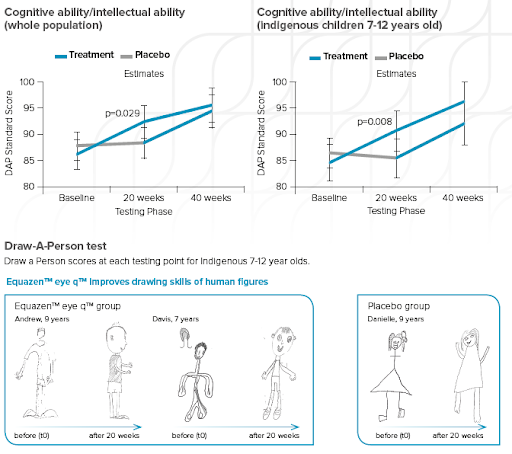
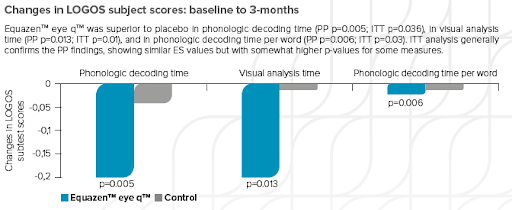
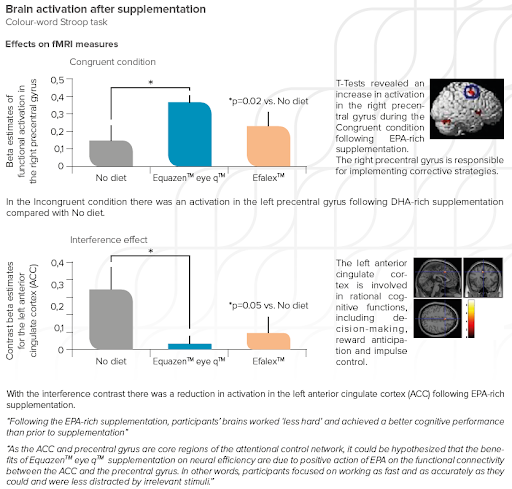
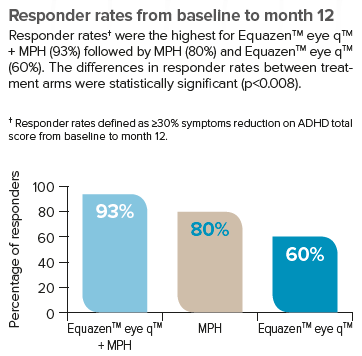
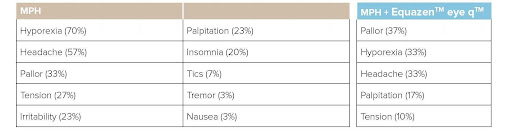
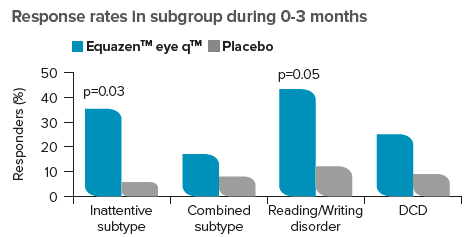
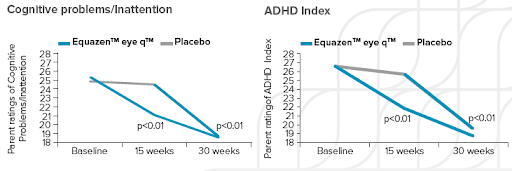
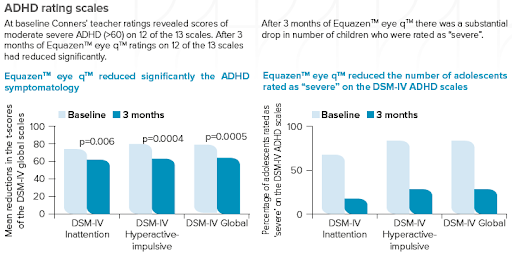
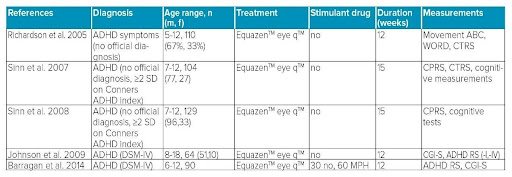
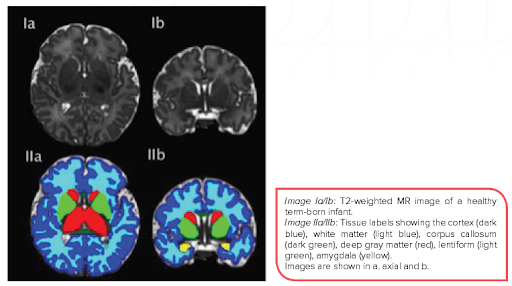
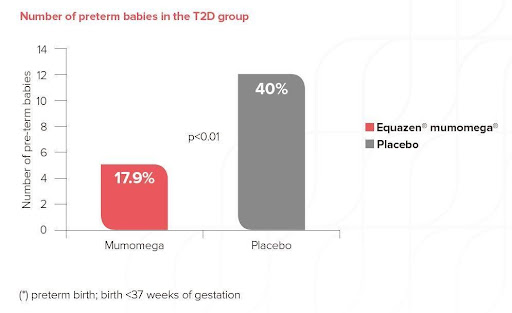
Equazen is developed with you in mind
Scientifically researched and sustainably sourced, Equazen is a simple way to get the natural benefits of fish oils in unique formulations that are tailored to suit you.
From infancy to adulthood, our bodies need different things. Which is why Equazen contain a different ratio of omega-3 EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid) and DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid) and omega-6 GLA (gamma-linolenic acid), depending on your nutritional needs at each life stage. We like to call it Equabalance. Equazen’s fish oils are carefully sourced from sustainable stocks. With a complete range of odourless capsules, liquids and flavoured chews, there’s something to suit every member of the family.




Equazen Family Capsules
Equazen Family Capsules is tasteless, odourless capsules for children to adults. Clinically researched formulation. Equazen Family Capsules provides you and your family with a unique formulation of high-grade omega-3 and omega-6 oils that has been produced following years of intensive scientific research Naturally-sourced and purified ingredients, formulated to a unique EQUABALANCE ratio. For 5 years to adult.
Details
Tasteless, odourless capsules for children to adolescents. Clinically researched formulation.
>8 clinical trials
13 years’ research
For 5 years to adult.
Essential Omega-3 & Omega- 6 fatty acids
2 capsules contain:
Fish Oil
-EPA 186 mg
-DHA 58 mg
Evening Primrose Oil
-GLA 20 mg
Starting dose: Take 6 capsules per day for the first 3 months
Maintenance dose: Take 2 capsules per day thereafter
- Do not exceed the recommended daily intake
- Consult your child’s doctor or pharmacist if your child is on any medication or if your child has any medical condition before starting supplementation
- Food supplements should not be used as a substitute for a well-balanced, varied diet and healthy lifestyle
Keep in a cool dry place
Keep out of Children’s reach
United Kingdom
Mannings Pharmacy Stores, Watsons Pharmacy Stores, Pharmacy Stores, Soda Mall (Prince Edward / Hung Hom), HKTVmall, Full Health Store


 中文 (中国)
中文 (中国) 中文 (香港)
中文 (香港)